

They are talking about fermentation (below).
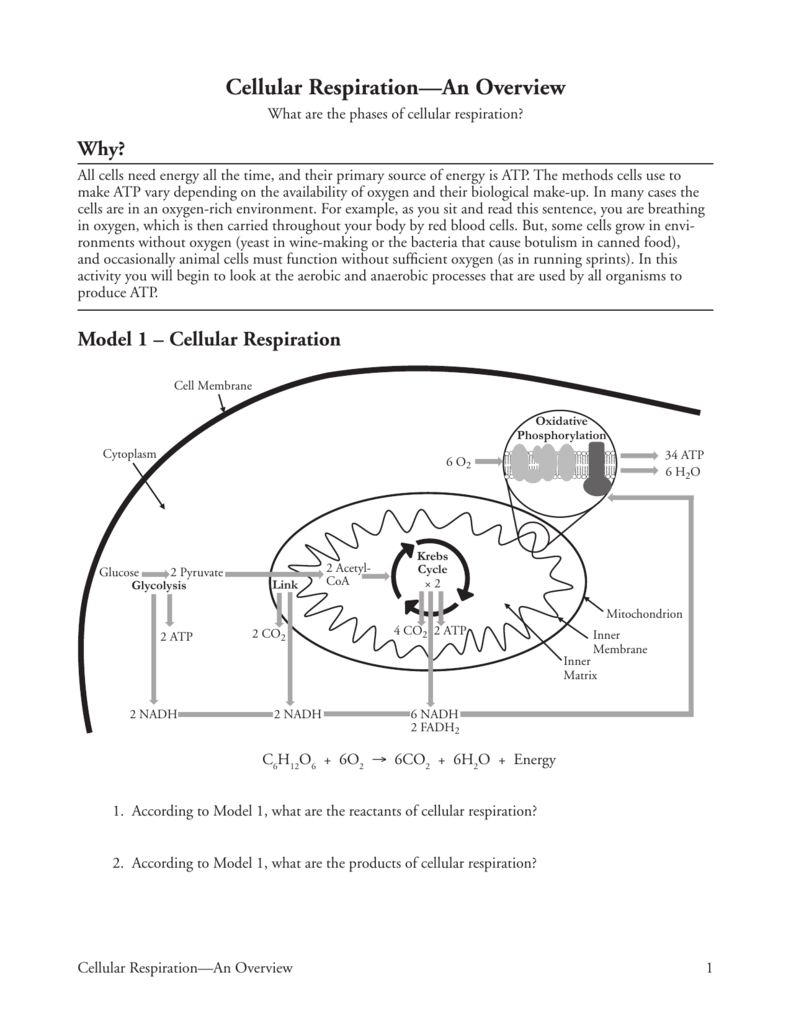
Just as a side note here, typically when “anaerobic respiration” is mentioned in videos and animations, they are not talking about this process. This is not a common form of cellular respiration and isn’t used by humans, so we will not be focusing on it. During anaerobic cellular respiration, cells use the same three basic stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain / chemiosmosis, but another molecule is used in place of oxygen gas. Some organisms (mostly bacteria) perform anaerobic cellular respiration. Video link: Cellular Respiration Anaerobic Processes Anaerobic Cellular Respiration The end result of this is the majority of ATP produced during aerobic respiration. The energy carrier molecules produced during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are used to power the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis (together known as oxidative phosphorylation).The carbon atoms are released as carbon dioxide. Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, where it is completely broken down into carbon dioxide and all the energy from the molecule is transferred to ATP and other energy carrier molecules.This leaves two 2-carbon molecules called acetyls, which are attached to Coenzyme A to make acetyl-CoA. One carbon atom is broken off of each of the two halves of the glucose molecule (3-carbon molecules known as pyruvate) and released as carbon dioxide.During glycolysis, 6-carbon glucose is broken in half and a small amount of energy is transferred to ATP and other energy carrier molecules.The next several sections in the textbook address the details of these stages, but here is a basic summary: This process has an overall release of energy which is captured and stored in 38 molecules of ATP.Īerobic respiration is a complex process that can be divided into three basic stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Translating that formula into English: One molecule of glucose can be broken down in the presence of oxygen gas to produce waste products of carbon dioxide (which we breathe out) and water.

The overall chemical formula for aerobic respiration can be written as:Ĭ 6H 12O 2+ 6 O 2 → 6 CO 2+ 6 H 2O + (approximately) 38 ATP Even some prokaryotes can perform aerobic respiration (although since prokaryotes don’t contain mitochondria, the reactions are slightly different). Aerobic respiration happens all the time in animals and plants, where most of the reactions occur in the mitochondria. This type of respiration releases a large amount of energy from glucose that can be stored as ATP. This is the reason why we breathe oxygen in from the air. Aerobic RespirationĪerobic respirationrequires oxygen. That means that during each of these enzyme-catalyzed reactions, some of the original energy from the sugar molecule is lost as heat. Every time energy is converted from one form to another, some of the energy is lost as heat. These processes require a large number of enzymes which each perform one specific chemical reaction.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION AN OVERVIEW SERIES
Glucose and other molecules from food are broken down to release energy in a complex series of chemical reactions that together are called cellular respiration.Ĭellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into ATP, and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
